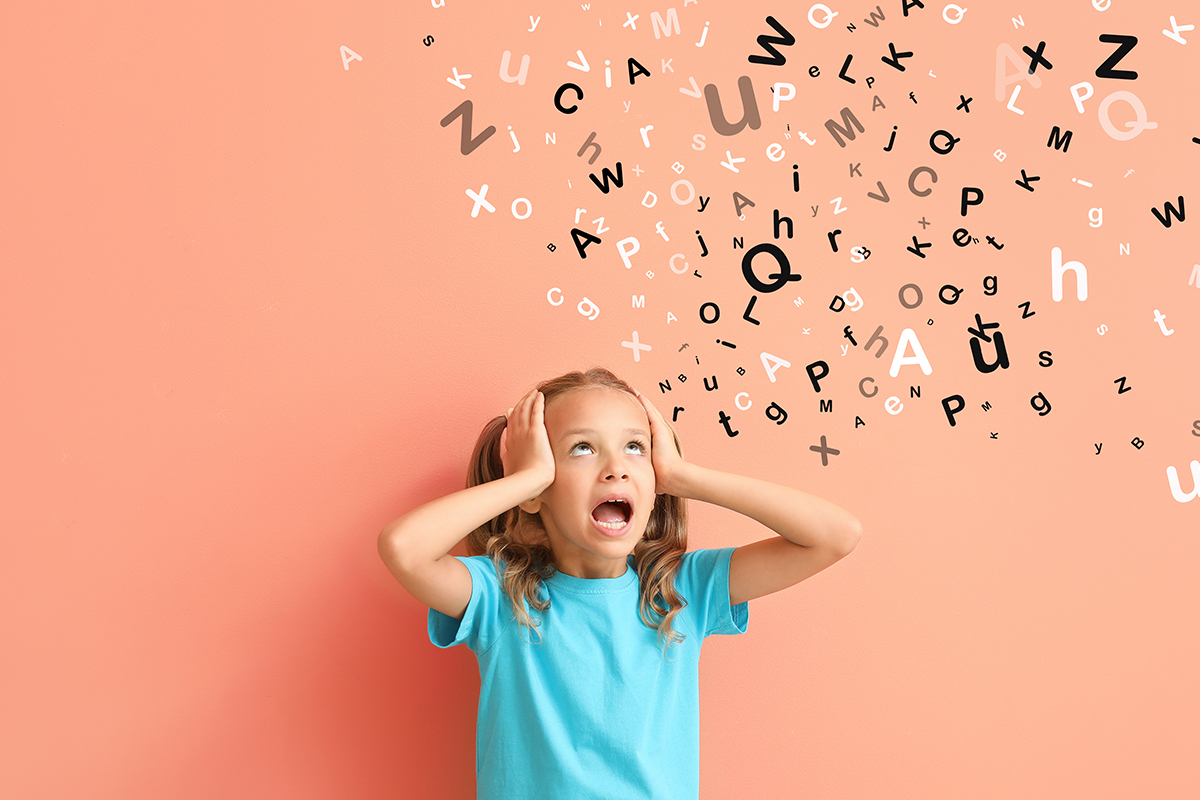
Dyslexia is what is known as a language-based learning disability. It presents various symptoms that cause difficulties with language skills, most commonly interfering with reading. In today’s blog post, we help improve Dyslexia Awareness, explaining everything you need to know about dyslexia and the treatments available.
What is Dyslexia?
Dyslexia is a learning disability impacting reading, spelling, writing, and word pronunciation.
Individuals with dyslexia will experience changes in how the condition affects their lives, especially during the academic years. As a learning disability, it makes it difficult for students to succeed, and in some cases, calls for special education accommodations to help students develop skills to cope with dyslexia.
What Causes Dyslexia?
It is still unclear what causes dyslexia.
However, it does appear that people with dyslexia have cognitive differences in how their brains develop and function. They also usually have someone in their family, such as a parent with dyslexia.
Moreover, people with dyslexia do not lack intelligence, as it impacts people of all intelligence levels. Often people with dyslexia are gifted with inherent skills, from music to math and design to computer science. In most cases, people can learn successfully once their disability is identified.
How Does Dyslexia Impact People?
Dyslexia affects people differently depending on the severity of their condition and whether they receive proper instruction or remediation.
For most people, their difficulties lie in word recognition and reading fluency. This, in turn, impacts their spelling and writing skills. When early interventions are introduced, students can develop reading and spelling coping strategies to complete tasks with less struggle.
However, without continued instruction, as the language they encounter becomes more complex, it can continue to present challenges without ongoing instruction. If spoken language is a factor, self-expression becomes difficult, leading to communication issues in school, work, and social situations. Spoken language can be more difficult to identify as dyslexia, which means it can continue into adulthood without intervention. For some, the stigma of dyslexia can cause confidence issues. This can lead to problems at school due to anxiety and poor self-esteem. As a result, some students might choose to leave school without pursuing higher educational opportunities.
How is Dyslexia Diagnosed?
Dyslexia is often suspected when students fail to meet expected benchmarks in reading.
Teachers track progress with basic screening tests to see if a student meets the expected benchmarks. When a student is consistently below that benchmark, individualized supplemental reading instruction is provided to see if a comprehensive evaluation is required.
The assessment determines whether a student needs a designation of special education eligibility. Prevention or early intervention can be very effective using Response to Intervention (RTI) methods. However, parents have a right to request a comprehensive evaluation under the IDEA law if they feel their child is not responsive to these interventions.
What is a Comprehensive Evaluation?
Comprehensive evaluations combine intellectual and academic achievement testing with an assessment of language skills impacted by dyslexia, including:
- Receptive (listening)
- Expressive language skills
- Phonological skills
- Ability to rapidly name letters and numbers
- Reading lists of words in isolation and context
These tests can help instructors spot characteristics of dyslexia so they can develop an individualized intervention plan.
What are the Signs of Dyslexia?
Signs of dyslexia in preschool children include:
- Late talking
- Slow to learn new words
- Problems forming words
- Problems remembering or naming letters, numbers, and colors
- Difficulty learning nursery rhymes or playing rhyming games
Learning Disabilities during school-aged years is one of the most common ways dyslexia is identified.
How is Dyslexia Treated?
Along with educational support, one-on-one or small group therapy can help build skills such as tutoring, educational therapy, executive functioning training through a learning specialist, and neurofeedback therapy.
As we venture deeper into the understanding of dyslexia, let’s take a moment to celebrate the complexity and resilience of the human mind. Each individual with dyslexia holds a unique constellation of strengths, talents, and potential, transcending mere labels or limitations. In cultivating awareness and acceptance, we pave the way towards a more inclusive, empathetic world where all forms of intelligence are valued and nurtured.
The Chicago Mind Solutions Difference
Chicago Mind Solutions works with individuals, offering neuropsychological testing and non-invasive treatment for many mental health conditions. For more information about our treatments and teletherapy options, please contact us at (224) 723-5050 or email info@chicagomindsolutions.com.